Game-Theoretic Centrality
The key idea behind game-theoretic centrality measures is to treat nodes as players in a cooperative game, where the value of each coalition of nodes is determined by certain graph-theoretic properties. The key advantage of this approach is that nodes are ranked not only according to their individual roles in the network but also according to how they contribute to the role played by all possible subsets (or groups) of nodes. This is important in various applications in which a group's performance cannot be simply described as the sum of the individual performances of the nodes involved.
To learn more please visit our dedicated website: www.game-theoretic-centrality.com
- “Efficient Algorithms for Game-Theoretic Betweenness Centrality”, accepted with minor revisions in Journal of Artificial Intelligence (AIJ) (with P.L. Szczepanski and T. Rahwan).
Impact factor (2014): 3.371.
- “A New Approach to Measure Social Capital Using Game-Theoretic Techniques”, Newsletter of the ACM Special Interest Group on E-commerce (ACM SIGecom Exchanges), vol. 14, no. 1, 2015, pp. 95-100, 2015 (with S. Moretti, R. Narayanam, O. Skibski, P. Szczepanski, T. Rahwan, and M. Wooldridge) (research letter).
Impact factor: not yet assigned.
- “Defeating Terrorist Networks with Game Theory”, IEEE Intelligent Systems, vol. 30, no. 1, 2015, pp. 53-61 (with T. Rahwan, O. Skibski and M. Wooldridge) (research letter).
Impact factor (2014): 2.340.
- “Implementation and Computation of a Value for Generalized Characteristic Function Games”, ACM Transactions on Economics and Computations (ACM TEAC) vol. 2, no. 4, 2014, pp. 16-43(with T. Rahwan, P. L. Szczepanski, A. Chrobak, S. Branzei, N.R. Jennings, and M. Wooldridge).
Impact factor: not yet assigned.
- “Efficient
Computation of the Shapley Value for Game-Theoretic Network Centrality”,
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research
(JAIR)
vol. 46, 2013, pp. 607-650 (with K. V. Aadithyaa, P. L. Szczepanski,
B. Ravindran and N.R. Jennings).
Impact factor (2014): 1.257. - “An Extension of the Owen-Value interaction index and Its Application to Inter-links Prediction” forthcoming in the Proceedings of the 21st European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2016) , Hague, The Netherlands (with P. Szczepanski, T. Rahwan, and M. Wooldridge). (acceptance rate of 27% our of more than 650 submissions).
- “Attachment Centrality: An Axiomatic Approach to Connectivity in Networks”, in the Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS 2016), Singapore, 9-13 May, 2016 (with Oskar Skibski, Talal Rahwan, and Makoto Yokoo) (137 papers accepted out of 550, acceptance rate 24.9%).
- “k-Coalitional Cooperative Games”, in the Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS 2016), Singapore, 9-13 May, 2016 (with Oskar Skibski, Szymon Matejczyk, Michael Wooldridge, Makoto Yokoo) (137 papers accepted out of 550, acceptance rate 24.9%).
- “A Pseudo-Polynomial Algorithm for Computing Power Indices in Graph-Restricted Weighted Voting Games”, in the Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2015), Buenos Aires, Argentina, on July 25-31, 2015 (with O. Skibski, Y. Sakurai, and M. Yokoo). (575 papers out of 1996 accepted, acceptance rate 28.8%).
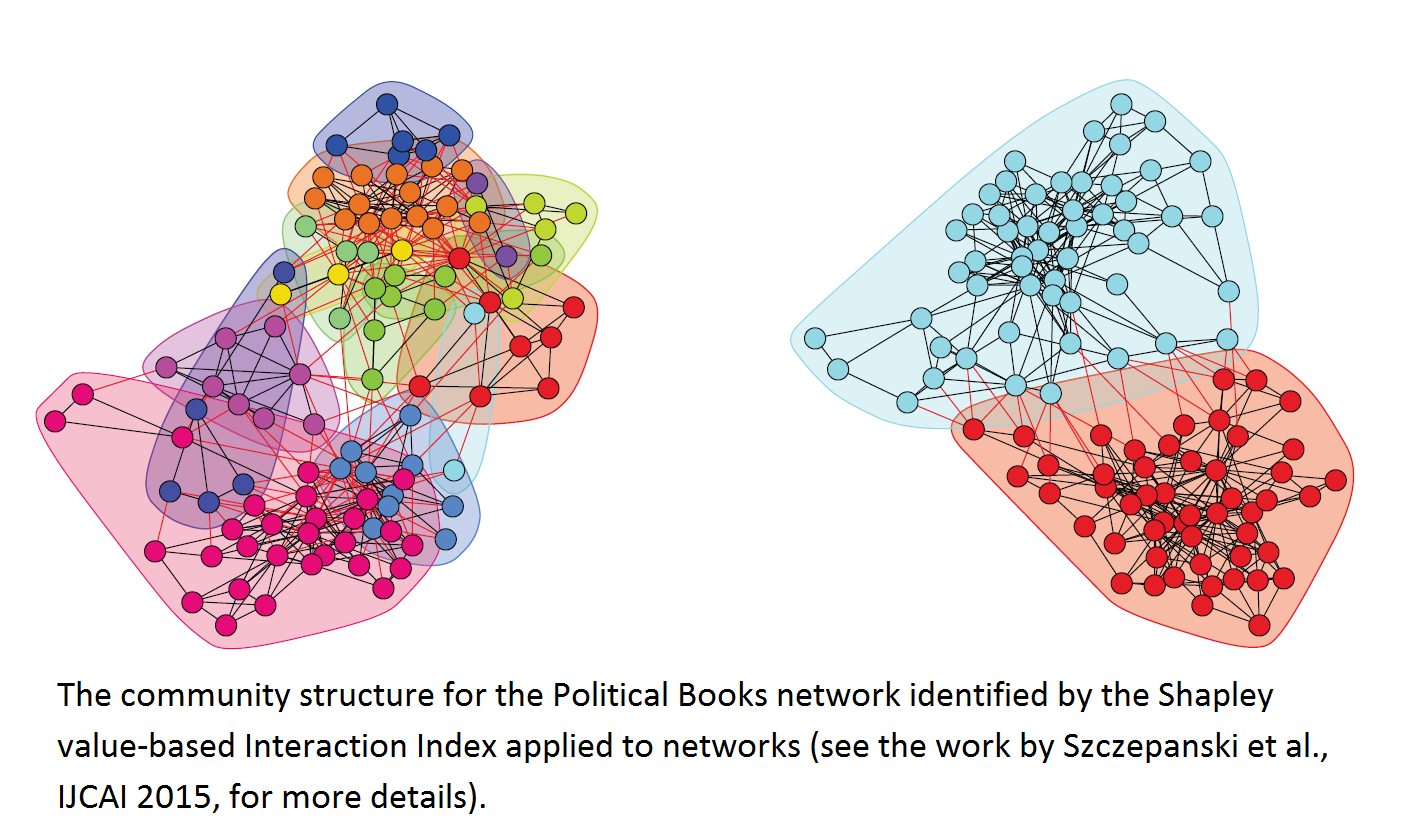
- “The Game-Theoretic Interaction Index on Social Networks With Applications to Link Prediction and Community Detection”, in the Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2015), Buenos Aires, Argentina, on July 25-31, 2015 (with P. Szczepanski, A. Barcz, T. Rahwan). (575 papers accepted out of 1996, acceptance rate 28.8%).
- “A Graphical Representation for Games in Partition Function Form”, in the Proceedings of the 29th Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2015), Austin, Texas, USA, pp. 1036-1042 (with O. Skibski, Y. Sakurai, M. Wooldridge, M. Yokoo). (acceptance rate 26.67%).
- “Closeness Centrality for Networks with Overlapping Community Structure”, in the Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2016), Phoenix, Arizona, USA (with M. Tarkowski, P. Szczepanski, T. Rahwan, and M. Wooldridge. (549 papers out of 2132 accepted, acceptance rate 25.8%).
- “Efficient Computation of Semivalues for Game-Theoretic Network Centrality”, in the Proceedings of the 29th Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2015), Austin, Texas, USA, pp. 461-269 (with P. L. Szczepański, M. Tarkowski, P. Harrenstein, and M. Wooldridge). (acceptance rate 26.67%).
- “A Centrality Measure for Networks With Community Structure Based on a Generalization of the Owen Value” in the Proceedings of the 21st European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2014) , Prague, Czech Republic, pp. 867-872 (with P. Szczepanski and M. Wooldridge). (158 papers accepted out of 562, acceptance rate 28%).
- “A Shapley Value-based Approach to Determine Gatekeepers in Social Networks with Applications”, in the Proceedings of the 21st European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2014) , Prague, Czech Republic, pp. 651-656 (with R. Narayanam, O. Skibski, H. Lamba). (158 papers accepted out of 562, acceptance rate 28%).
- “Algorithms for Myerson and Shapley Values for Graph-restricted Games", in the Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS 2014), Paris, France, 5-9 May, 2014 (with Oskar Skibski, Talal Rahwan and Michael Wooldridge) (169 papers accepted out of 709, acceptance rate 23.8%).
- “Computational Analysis of Connectivity Games with Applications to Terrorist Networks", in the Proceedings of International Conferences on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2013), Beijing, China, on August 3-9, 2013. (with Talal Rahwan, Piotr Szczepanski, Oskar Skibski, Ramasuri Narayanam, Nick Jennings, Michael Wooldridge) (413 papers acceped out of 1473, acceptance rate 28%).
- “A New Approach to Betweenness Centrality Based on the Shapley Value”, in the Proceedings of 11th Int. Conf. on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2012), Valencia, Spain (with P. Szczepanski and T. Rahwan) (acceptance rate 20.4%).
- “Efficient Computation of the Shapley Value for Centrality in Networks” in the Proceedings of the the 6th Workshop on Internet & Network Economics (WINE 2010), Stanford University, Palo Alto, USA, (with K. Aadithya, B. Ravindran and N.R. Jennings) (acceptance rate 27%).
Coalition Structure Generation
The coalition structure generation problem is a natural abstraction of one of the most important challenges in multi-agent systems: How can a number of agents divide themselves into groups in order to improve their performance? More precisely, the coalition structure generation problem focuses on partitioning the set of agents into mutually disjoint coalitions so that the total reward from the resulting coalitions is maximized. This problem is computationally challenging, even under quite restrictive assumptions. This has prompted researchers to develop a range of algorithms and heuristic approaches for solving the problem efficiently.
- “Coalition Structure Generation: A Survey”, Journal of Artificial Intelligence (AIJ), vol. 229, 2015, pp. 139–174 (with T. Rahwan, M. Wooldridge and N. R. Jennings).
- Impact factor (2014): 3.371
- “An Exact Algorithm for Complete Set Partitioning”, forthcoming in Journal of Artificial Intelligence (AIJ) (with T. Rahwan, E. Elkind, M. Wooldridge and N. R. Jennings).
- Impact factor (2014): 3.371
- “Anytime Coalition Structure Generation in Multi-Agent Systems with Positive or Negative Externalities”, in Journal of Artificial Intelligence (AIJ) vol. 186, 2012, pp. 95-122 (with T. Rahwan, M. Wooldridge and N. R. Jennings).
- Impact factor (2014): 3.371
- “Coalition Structure Generation with the Graphics Processing Unit", the Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS 2014), Paris, France, 5-9 May, 2014 (with Krzysztof Pawlowski, Karol Kurach, Kim Svensson, Sarvapali Ramchurn, and Talal Rahwan).
- A23.8% (169 papers accepted out of 709)
- “Coalitional Games via Network Flows", in the Proceedings of International Conferences on Artificial Inteligence, (IJCAI 2013), Beijing, China, on August 3-9, 2013. (with Talal Rahwan, Tri-Dung Nguyen, Maria Polukarov, Madalina Croitoru, Michael Wooldridge, Nick Jennings).
- Acceptance rate: 28% (413 papers accepted out of 1473)
- “A Hybrid Algorithm for Coalition Structure Generation”, in the Proceedings of 26th Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2012), Toronto, Canada, pp. 1443-1449 (with T. Rahwan and N. R. Jennings).
- Acceptance rate: 26%
- “Constrained Coalition Formation”, in the Proceedings of 25th Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2011), San Francisco, USA. (with T. Rahwan, E. Elkind, P. Faliszewski, J. Sroka, M. Wooldridge and N. R. Jennings).
- Acceptance rate: 24.8%
- “Minimum Search To Establish Worst-Case Guarantees in Coalition Structure Generation”, in the Proceedings of International Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, (IJCAI 2011), Barcelona, Spain. (with T. Rahwan, and N. R. Jennings).
- Acceptance rate: 17%
- “A Distributed Algorithm for Anytime Coalition Structure Generation”, in the Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2010), van der Hoek, Kaminka, Lespérance, Luck and Sen (eds.), Toronto, Canada, (with J. Sroka, T. Rahwan, P. McBurney, M. Wooldridge and N.R. Jennings).
- Acceptance rate: 24%
- “On representing coalitional games with externalities”, in the Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Electronic Commerce (ACM EC 2009), pages 11–20, New York, NY, USA. (with T. Rahwan, J. Sroka, A. Dowell, M. J. Wooldridge, P. J. McBurney, and N. R. Jennings).
- Acceptance rate: 25%
- “Coalition structure generation in multi-agent systems with positive and negative externalities.” in the Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, (IJCAI 2009), Pasadena, USA. (with T. Rahwan, N. R. Jennings, M. Wooldridge, and P. McBurney).
- Acceptance rate: 26%
- “Optimal Coalition Structure Generation in Partition Function Games”, in the Proceedings of 18th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI 2008), Patras, Greece, (with A. Dowell, P. McBurney and M. Wooldridge).
- Acceptance rate: 21.5%
Dollar Auction & Conflict Escalation
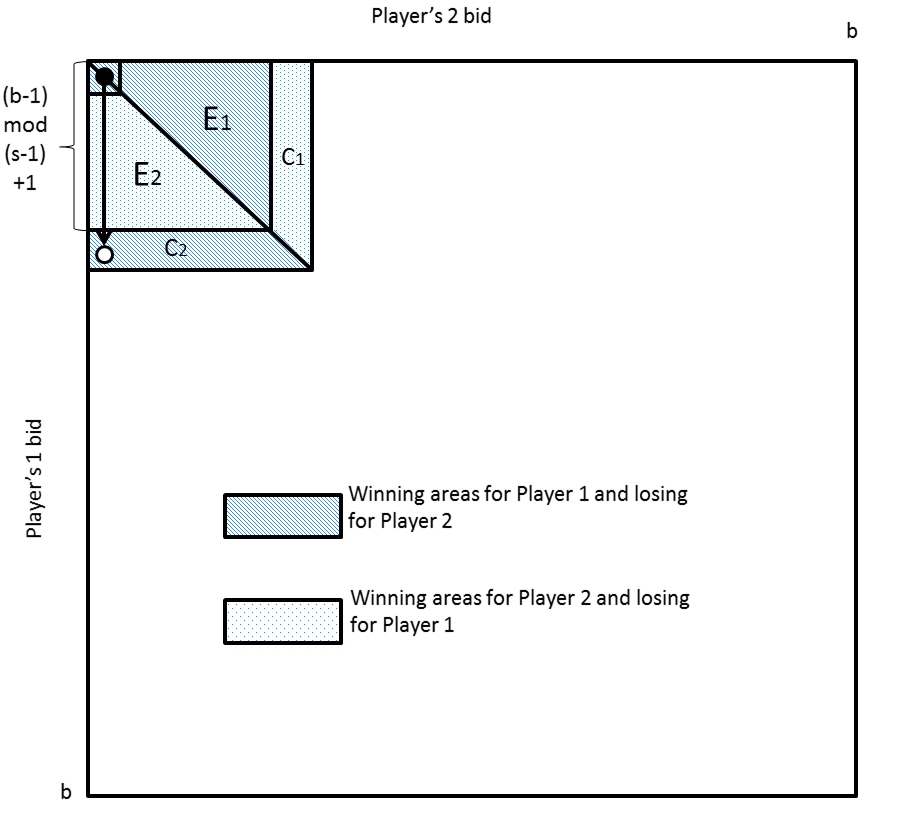
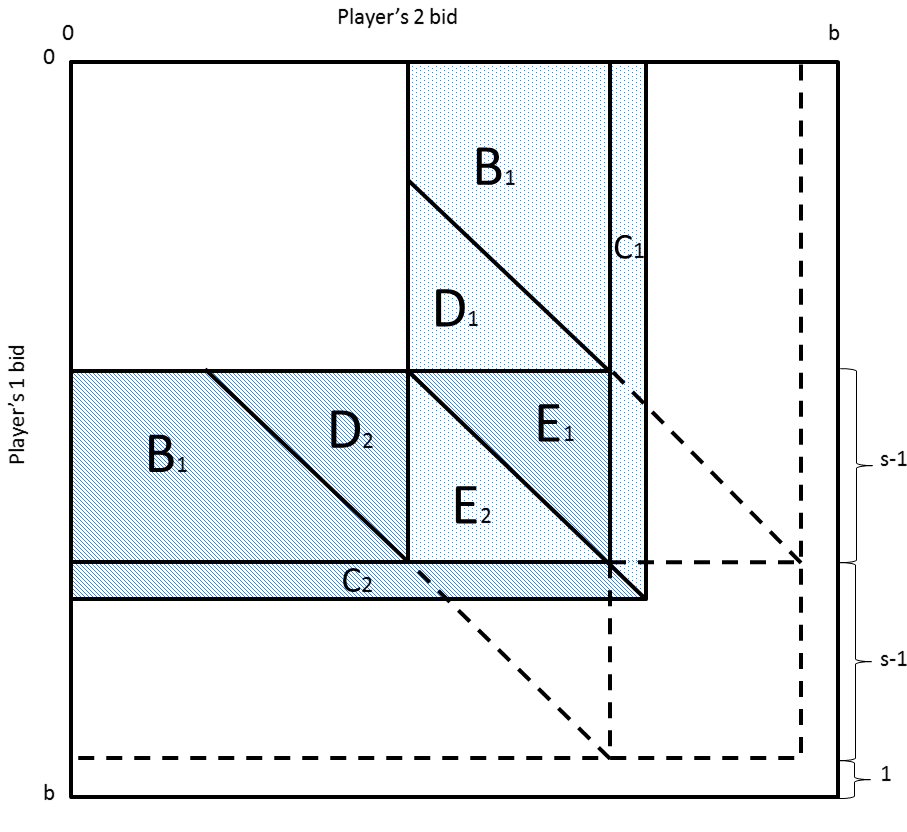
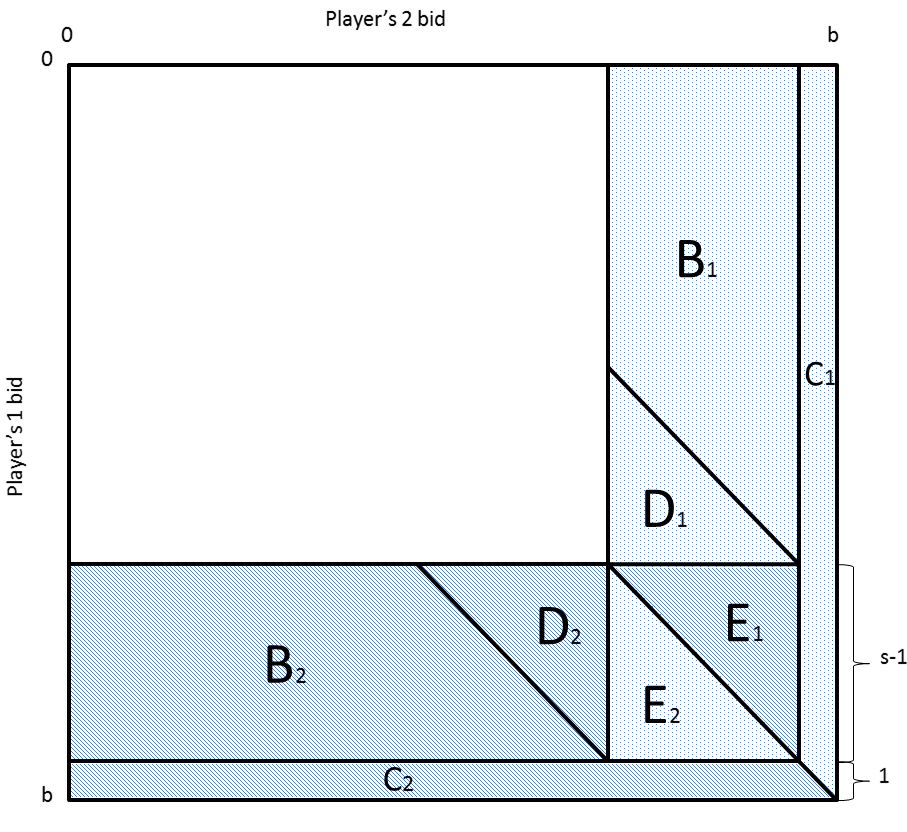
Shubik’s dollar auction is a simple yet powerful all-pay auction model that aims to shed light on the motives and dynamics of conflict escalation. In this auction, two bidders i and j compete for a dollar; the highest bidder wins the prize, but both the winner and the loser have to pay their bids to the auctioneer. The dollar auction game has become an influential abstraction of conflict escalation processes. It shows that conflicts may reach irrational levels despite the fact that, locally, every single participant makes a rational decision.
In his beautiful paper, O’Neill [1986] offered a surprising solution to the dollar auction—he proved that, assuming finite budgets of players, in all equilibria in pure strategies, only one player bids and wins the prize. The exact amount of such a “golden” bid is a non-trivial function of the stake, the budgets, and the minimum allowable increment.
- “Repeated dollar auctions: A multi-armed bandit approach”, in the Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (AAMAS 2016), Singapore, 9-13 May, 2016 (with Marcin Waniek, Long Tran-Thanh, Talal Rahwan) (137 papers accepted out of 550, acceptance rate 24.9%).
- “Spiteful Bidding in the Dollar Auction”, in the Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2015), Buenos Aires, Argentina, on July 25-31, 2015 (with M. Waniek, A. Niescieruk, and T. Rahwan). (575 papers out of 1996 accepted, acceptance rate 28.8%).